1.0 Installation
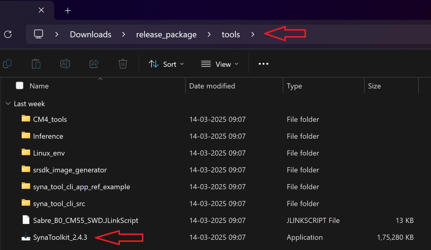
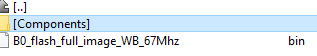
Use SynaTool Kit from Release package: <SRSDK>/tools/
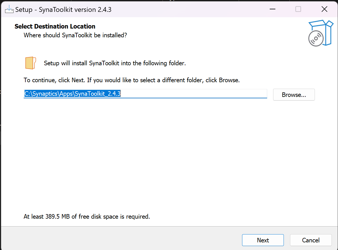
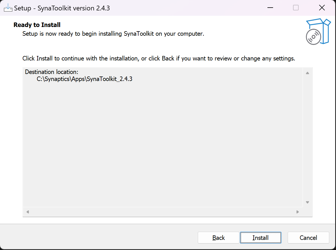
Run SynaToolkit installer and follow the instructions:
The default installation folder for SynaToolkit is: C:SynapticsAppsSynaToolkit_2.4.3
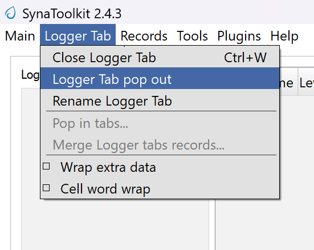
3.0 Logger Functionality
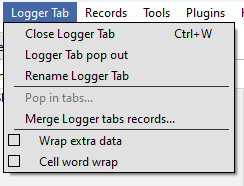
3.1 Logger Connect/Disconnect
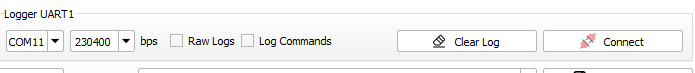
Purpose: Facilitates the connection and disconnection of the Logger tool to and from UART1 Com ports, allowing for dynamic logging of system communications.
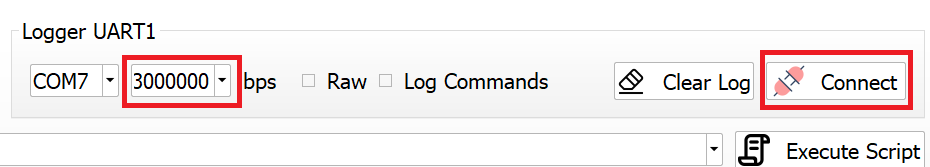
3.1.1 Connect
To Connect: Select the appropriate UART1 Com port and baud rate, then click the Connect button. A new Logger tab will open for each connection, displaying incoming log data.
Requirements: Ensure the correct COM port and baud rate are selected to establish a successful connection.
3.1.2 Disconnect
To Disconnect: Press the Disconnect button to terminate the connection with the logger.
Tab Persistence: The Logger tab will remain open and accessible even after disconnection, allowing you to review the logged data.
3.1.3 Clear Log
Functionality: Clears all data from the log buffer to free up space or prepare for new data.
Usage: Click the Clear Log button to remove all existing entries from the log display.
3.1.4 Raw Logs
Overview: If enabled, the logger will display logs without parsing them according to the SR110 format, showing raw data as received.
Toggle: Check the Raw Logs box to view unprocessed log entries.
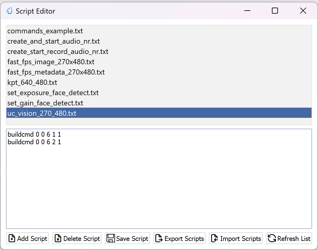
3.1.5 Log Commands
Functionality: When checked, commands executed through SynaTool are logged, providing a transcript of actions performed during the session.
Activation: Check the Log Commands box to include command logging in the session data.
Usage Notes:
Utilizing the Logger effectively can aid in troubleshooting and monitoring the system’s communication with connected devices.
Ensure that logs are saved or cleared appropriately to avoid loss of important data or overflow that could hinder performance.
3.2 Log NameSpaces
Purpose: Allows users to select different namespaces related to supported chips and cores, facilitating targeted logging sessions specific to hardware components.
Functionality:
Currently, the tool supports logging for the SR110 chip with core M55, M4, with the potential to expand to other chips and cores in the future.
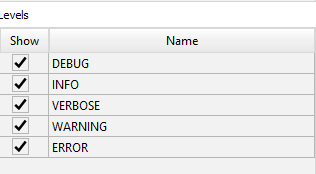
3.3 Levels
Purpose: Provides a customizable logging experience by allowing users to select which levels of log messages (such as Errors, Warnings, or Debug information) are visible.
Features:
Selective Visibility: Toggle visibility of log messages by level to focus on relevant data, such as debugging information or errors.
Customize Appearance: Modify the appearance of log messages by level for better readability or personal preference.
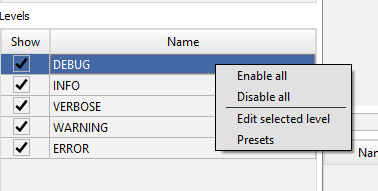
If you focus on one of the level with mouse and press right button the new windows will be popup where you can select one of options:
3.3.1 Enabling/Disabling Levels
Access: Right-click on any level in the levels window to access options.
Options:
Enable All: Show all log levels.
Disable All: Hide all log levels.
Edit Selected Level: Open the level editor to change properties such as color and font style.
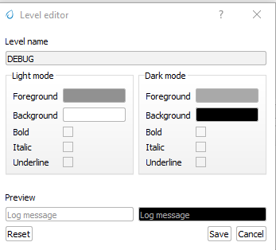
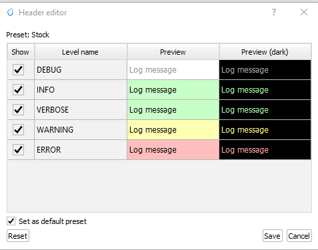
3.3.2 Level Editor
Functionality: Customize the visual properties of log messages for each level.
Settings:
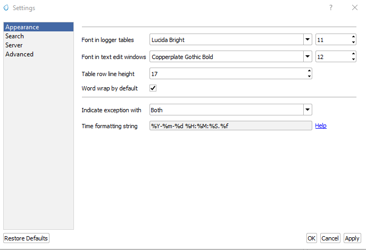
Light/Dark Mode Color Settings: Adjust text and background colors for both light and dark modes.
Font Styles: Change font styles including bold, italic, and underline.
Preview: View changes in real-time within the preview pane at the bottom of the level editor window.
3.3.3 Presets
Purpose: Quickly apply predefined or custom styling presets to log levels.
Usage:
Set as Default Preset: Apply the selected preset as the default for all log levels.
Reset to Default: Revert to the application’s default preset settings.
Usage Tips:
Utilize the log namespace feature to manage logs according to specific hardware components or software modules.
Adjust log levels to streamline the debugging process, focusing only on the necessary data.
Customize log appearance to differentiate between log types easily or match user preferences for an enhanced visual experience.
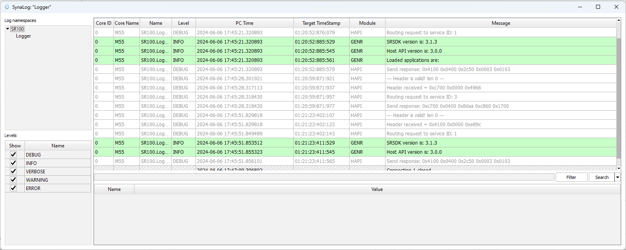
3.4 Main Log Window
Purpose: The Main Log Window is central to viewing and managing log data, offering a variety of tools to enhance the visibility and analysis of log messages.
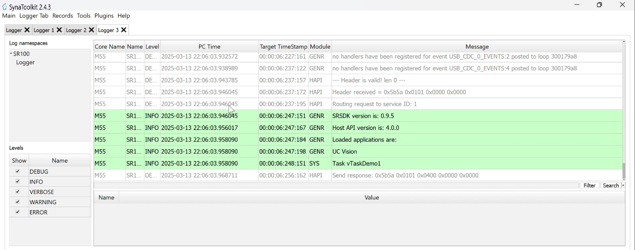
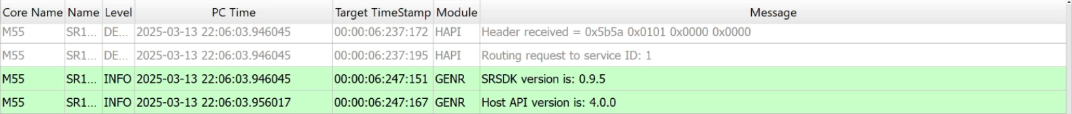
3.4.1 Log Display
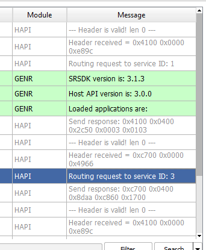
Overview: Displays logs with detailed information such as Core Name, Log Namespace, PC Time, Target Timestamp, Module, and the message itself.
Navigation: Logs are shown in a tabulated format allowing for easy review and management.
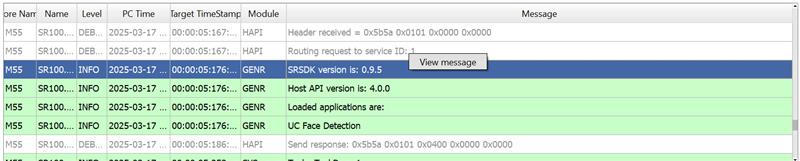
3.4.2 Message Details
Accessing Details: Right-click on a message and select “View message” to open a detailed view of the log message.
Usage: This feature is useful for examining complete log entries in depth.
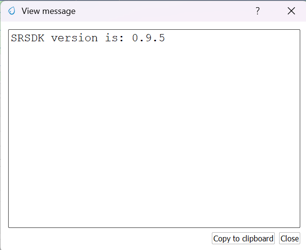
3.4.3 View Message Window
Functionality: Displays the complete content of a log message.
Options: Users can copy the message to the clipboard or close the window.
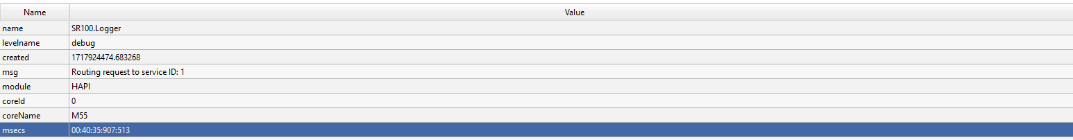
3.4.4 Parsed Message Display
Description: Shows a parsed view of the message, breaking down the log entry into its components like Name, Level, Time, and Message, among others.
Interactivity: This detailed view helps in understanding the structured components of each log message.
3.4.5 Filtering Logs
Filtering: Enter specific criteria in the filter bar to display only those log entries that meet the conditions.
Resetting Filter: Clear the filter by pressing the “Clear Filter” button to return to viewing all logs.
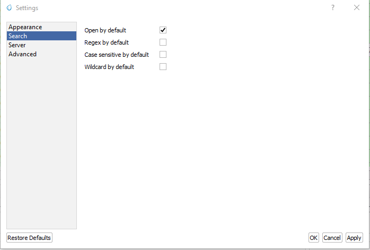
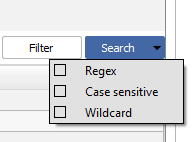
3.4.6 Search Functionality
Capabilities:
Regex (Regular Expression): Use regex for complex pattern searches within log messages.
Case Sensitive: Search the logs taking into account the case sensitivity.
Wildcard: Use wildcard characters to search for variations of a string.
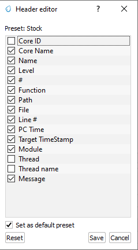
3.4.7 Customize Header
Customization: Right-click on any column header to customize which data columns are displayed.
Header Editor:
Adjust Visibility: Toggle various data points like Core ID, Function, Thread Name, etc., to show or hide in the log view.
Save/Reset: Save the custom settings as the default or reset to the stock configuration.
Tips for Effective Use:
Utilize the detailed message view to troubleshoot specific issues by examining the full content of relevant logs.
Regularly clear and filter logs to maintain clarity and focus on relevant entries during analysis.
Customize the log display headers to focus on information pertinent to your analysis needs.